- The other side of broken windows Eric Klinenberg, New Yorker
- “Peace through strength” is weakening Putin at home Krishnadev Calamur, the Atlantic
- How to cleanse the Catholic Church Andrew Sullivan, Daily Intelligencer
- The garment of terrorism Azadeh Moaveni, London Review of Books
Month: August 2018
Nightcap
- Why Czechs don’t speak German Jacklyn Janeksela, BBC
- The Kurds, Sykes-Picot and the quest for redrawing borders Nick Danforth, BPC
- The language of the economy: prices Rick Weber, NOL
- A Balkan border change the West should welcome Marko Prelec, Politico EU
Nightcap
- Yoram Hazony and the New Nationalism Samuel Goldman, Modern Age
- The archive of comics sponsored by South Africa’s Apartheid government William Worger (interview), Africa is a Country
- Photo essay on the Soviet squelching of the Prague Spring Alan Taylor, the Atlantic
- Failed states and failed civilizations Nick Nielsen, The View from Oregon
Nightcap
- Confucianism and meritocracy James Hankins, American Affairs
- Lots of ideological axes to grind Scott Sumner, EconLog
- Did the notorious Zinoviev Letter ever exist? Alan Judd, Spectator
- That time when Chile conquered Peru and Bolivia Stefan Aguirre Quiroga, History Today
Between anarchy and minarchism
While sometimes we think of ideologies in strict terms of left and right, more and more frequently we look at political schemas that incorporate a dimension for statism. Big government is possible for both conservatives and progressives; so, maybe, is minarchy. If minarchy is possible, and achievable, it must attain popular support less it be thwarted by revolution or contrarian voting. From this, maybe it makes sense that a minarchism utilize fundamental values from each side, in order to be pragmatic and achieve democratic (and thereby maybe stable) ends. Here there may even be room for an ultraminarchy.
In Anarchy, State and Utopia, Robert Nozick defended a minimal state slightly more restrained than traditional classical liberalism. This minimal state arises through natural market forces from statelessness, and serves to enforce contracts and produce monopolistic law. Nozick, although countering his fellow Harvard academic Rawls, was also responding to the natural law anarchists, who criticized coercive states for violating human rights — which, in the American tradition, often boil down to rights of property and self-ownership.
However, before arriving at the minimal, night-watchman state, Nozick articulates an ultraminimal state, i.e. a private protection agency that claims exclusionary right over the use of force for a given geographical area. It has its voluntary clients; the extension of coverage to others makes the agency a “state” as it introduces taxation.
In ASU the state is an entity formed from an invisible hand to produce heavily right-libertarian functions of government like protecting negative rights. Because of this, the minarchist state was a refuge for archist libertarians to claim as their own, relatively consistent with centuries of Western liberal thought. Accordingly, in response, the anarchists question the viability of a lasting minimal state — cue David Friedman in Machinery of Freedom:
“It took about 150 years, starting with a Bill of Rights that reserved to the states and the people all powers not explicitly delegated to the federal government, to produce a Supreme Court willing to rule that growing corn to feed to your own hogs is instate commerce and can therefore be regulated by Congress.”
Government grows; modern government grows really, really fast. Minimalism hasn’t seemed to last. So the question is, what sorts of minimal governance could last?
The traditional ultraminimal and minimal state are concerned with, as stated, traditionally libertarian public functions such as police, the judiciary, and possibly roads and maybe even national defense. The problem with these utilities is that they feel wildly inadequate to the modern American used to entitlements, welfare, or, e.g., a president. The privatization of nearly all federal departments — even when their failures are widely acknowledged — is seen as wild enough for John Oliver to entertain millions of viewers, at the blight of Gary Johnson, and make hardcore eliminativism a losing electoral program. The contemporary world is too complicated, or our enemies are too powerful, or the market is too corrupt for the reinstitution of laissez-faire in the 21st century.
Nevertheless we want a smaller government, or no government, and losing to the tide isn’t a good death; we’d rather fight, and we’d rather win. A lasting minarchism satisfies the broad purposes of limited governance — basic liberty, protection, and preserving the benefits of the market — while sufficiently completing modern democratic demands, lest it erode into statism or collapse internally. (Keep in mind that statelessness, at least this week, is not a winning platform.)
Here’s what I think lies between anarchism and minarchism: the redistributive state. We can make a couple assumptions which I think are likely true: (1) every public service, including public goods, currently monopolized by the state could be provided (and, maybe, could be provided better) by the market and non-coercive communities instead, and (2) the entitlement theory of distributive justice offered by Nozick is correct, i.e. holdings are just if acquired by peaceful initial acquisition, voluntary exchange or gifting, or rectification of a previous unjust acquisition. Taking these assumptions, and leveraging the fact that the American populace will not currently settle for brutalist governance, the redistributive state (RS) seeks only to collect tax revenues and redistribute money progressively.
Instead of offering vouchers, EBT, or public options like housing, schools, security and roads, a RS would only tax its citizens and reallocate revenue based on some progressive variables like income, net worth or consumption. (These details are less important, for now.) The only administration is something like an Internal Revenue Service, Census Bureau, and investigation unit suffused together, with over ninety-five percent of the current staff eliminated, with tax escapees adjudicated through non-state means.
An RS violates rights based on a Lockean or Kantian conception; it also does something which sounds pretty socialist to right-wing circles. For this reason, though minarchist, it may not be libertarian. However, the pragmatic element is also very utilitarian and liberal, which may interest bleeding-hearts; and, being essentially one big welfare program, it may intrigue American leftists currently eyeing a state takeover of health care and socialized education. We would do well to keep in mind that Friedrich Hayek and Milton Friedman were not averse to basic income either — a redistributive state operates a universal basic allowance and abandons the productive functions of the state. I think it is generally clear that, in a situation where we are already giving a person $X in the illiquid form of schools, transfer payments, utilities, roads, defense, firefighters, social planning, arts, retirement investing, mail service, etc., instead we should just give that person $X to spend however they see fit, to reap more competitive pressure from consumer exposure to prices and to align their dollars with their own individual values. If anyone disagrees, they might be too top-down to consider minarchism in any scenario.
The RS has many benefits over our current, vague understanding of contemporary government. In the first case, the reductionist perspective of right-wing anarchists, such as the stationary bandits theory, is validated, and a lot of the mysterious machinery and ivory-tower political philosophy is dissolved. Some of the bright spots of recent cameral formalist thought are validated, too, without the unpleasant baggage. (And armchair philosophizing about the Rousseauian general will is finally put to rest.) And, for the Marxists, their critique of the state as a tool of the capitalist class, which is true enough, is answered, since the state now greatly serves labor more than capital: some of the income of the upper classes is directly confiscated from them and allocated to the lower classes. Also, the state ceases to be paternalistic — it no longer chooses what food is available through SNAP, or issues health and safety warnings; it just straight-up hands out the money without assuming value for consumers. It doesn’t determine what is taught in schools, or what color the roads are, or which country gets bombed on Tuesday.
Perhaps most popularly, the RS has the potential to all but eliminate bureaucracy. With one small administrative branch which functions like a hyper-specialized agency, there is little room or need for massive proliferation and government by permanent staffers, where we find ourselves now. Likely, all seats will be elected positions along with some underlings, with the marginal tax brackets pre-established constitutionally and open to a similar amendment process. But, that can all be figured out later.
Now, there are some obvious flaws for an RS. First of all, the very wealthy, prima facie, have little incentive to stay in a redistributive state. Their money is seized and without tangible benefit for themselves, like roads or security. They have to buy those things on their own dime. The redistributive state is the antithesis of Galt’s Gulch. The primary answer to this I can think of is that, in a society with less state omnipotence (in contrast to today, where everyone’s first answer to a problem starts with a “g”) community ties will be closer — the rich will want to pay their “fair share.” This is the Hoppean trust in private charity, except that it’s now “forced private” charity. Also, taxes would be much, much lower than the current situation and hopefully tolerable. The taxes are also going directly to other citizens instead of politician’s wallets, oil tycoons, and potassium chloride. Furthermore, they’re paying to live in — the government still has a coercive and unjustified monopoly on land — the freest nation in the world. An RS is significantly freer than the other statist regimes, and less stressful. Government plays no role at all in everyday life.
One other flaw — maybe an inherent flaw of government brightly illuminated by a raw redistributive state — is what Murray Rothbard saw as an eternal tension between net tax-payers and net tax-consumers. To the extent that the RS administration is elected, and to the extent that politicians have platforms, a lot rests on whether or not taxes will be raised (read: redistribution will increase) or not. The left will continually be concerned with income inequality, regardless of whether or not everyone is well-off. The goalposts might keep climbing, to where taxation is no longer about fairness or the difference principle, but about punishment. At the same time, dialectically, the very wealthy will want to keep the maximum amount of their money and protect profit, regardless of my arguments above. Raw societal tensions like these probably require a dynamic form of governance, with fluctuations in party dominance, but the RS is too brutalist to feature such parties or other contrivances. The only hope here, I guess, is that the tension will be less than in the current system we have, where people openly talk about murdering the other party. And very likely it will be. (Also, the market will correct much of the gratuitous wealth disparity presently built upon rent-seeking — so it becomes an empirical question about what levels of inequality create what levels of tension, as there will be large inequality in any non-patterned system of holdings.)
In conclusion, a redistributive state would be baldly organized around theft (in a libertarian interpretation) and using people as means rather than ends. To that extent it is hardly libertarian. It achieves Nozick’s end of minimal government but distorts the typical functions we correlate with small government. Still, it’s ultraminarchical, preserves innovation, balances right-wing virtues like liberty and industry and left-wing virtues like equality and positive freedom, and, for a radical populace not quite keen on revolution, has the potential to be politically attractive. It serves welfarist functions demanded by 21st century citizens without the corporatist empire of the present. Also, no one starves. For all of this, even if a redistributive state is not perfection incarnate, it seems far better than the current system, and provides a culturally-celibate political framework to possibly achieve success in totally disparate societies from the United States. I think it’s a useful, radical place to look for bipartisan solutions to a complicated and overwhelmingly statist world.
I’m pretty sure I’m the first one to suggest a state organized baldly and singularly around redistribution of private income, either because it’s too stupid or it’s too grossly unattractive, so I welcome all feedback. But, if voluntarist alternatives are possible at all, this implies all the state is is a redistributor anyway. The idea of an RS just accepts this conclusion and makes it efficient. Keep in mind I haven’t elaborated on the many complications of UBI, which is an entire field to articulate more extensively, and which has its own numerous difficulties. For now the only question is would this form of government be possible.
Nightcap
- Soccer, communists, fascists, and Yugoslavia Richard Mills (interview), Jacobin
- Over- and under-reactions in politics Chris Dillow, Stumbling & Mumbling
- How a controversial non-violent movement has transformed the Israeli-Palestinian debate Nathan Thrall, Guardian
- Sovereignty, confusion, and the international order Nick Danforth, War on the Rocks
The Real Cost of National Health Care
Around early August 2018, a research paper from the Mercatus Center at George Mason University by Charles Blahous made both the Wall Street Journal and Fox News within two days. It also attracted attention widely in other media. Later, I thought I heard sighs of satisfaction from conservative callers on talk show radio whenever the paper came up.
One figure from the study came and stayed at the surface and was quoted correctly many times (rare occurrence) in the electronic media. The cost of what Senator Sanders proposed with respect to national health care was:
30 trillion US dollars over ten years (actually, 32.6 over thirteen years).
This enormous number elicited pleasure among conservatives because it seemed to underscore the folly of Senator Bernie Sanders’ call for universal healthcare. It meant implicitly, federal, single-payer, government-organized health care. It might be achieved simply by enrolling everyone in Medicare. I thought I could hear snickers of relief among my conservative friends because of the seeming absurdity of the gigantic figure. I believe that’s premature. Large numbers aren’t always all they appear to be.
Let’s divide equally the total estimate over ten years. That’s three trillion dollars per year. It’s also a little more than $10,000 per American man, woman, child, and others, etc.
For the first year of the plan, Sanders’ universal health care amounts to 17.5% of GDP per capita. GDP per capita is a poor but not so bad, really, measure of production. It’s also used to express average gross income. (I think that those who criticize this use of GDP per capita don’t have a substitute to propose that normal human beings understand, or wish to understand.) So it’s 17.5% of GDP/capita. The person who is exactly in the middle of the distribution of American income would have to spend 17.5% of her income on health care, income before taxes and such. That’s a lot of money.
Or, is it?
Let’s imagine economic growth (GDP growth) of 3% per years. It’s optimistic but it’s what conservatives like me think is a realistic target for sustained performance. From 1950 to 1990, GDP per capita growth reached or exceeded 3% for almost all years. It greatly exceeded 3% for several years. I am too lazy to do the arithmetic but I would be bet that the mean annual GDP growth for that forty-year period was well above 3%. So, it’s realistic and probably even modest.
At this 3% growth rate, in the tenth year, the US GDP per capita will be $76.600. At that point, federal universal health care will cost – unless it improves and thus becomes more costly – 13% of GDP per capita. This sounds downright reasonable, especially in view of the rapid aging of the American population.
Now, American conservative enemies of nationalized health care are quick to find instances of dysfunctions of such healthcare delivery systems in other countries. The UK system was the original example and as such, it accumulated mistakes. More recently, we have delighted in Canadian citizens crossing the border for an urgent heart operation their nationalized system could not produce for months: Arrive on Friday evening in a pleasant American resort. Have a good but reasonable dinner. Check in Sat morning. Get the new valve on Monday; back to Canada on Wednesday. At work on the next Monday morning!
The subtext is that many Canadians die because of a shortage of that great free health care: It nice if you can get it, we think. Of course, ragging on the Canadians is both fair and endlessly pleasant. Their unfailing smugness in such matters is like a hunting permit for mental cruelty!
In fact, though, my fellow conservatives don’t seem to make much of an effort to find national health systems that actually work. Sweden has one, Denmark has one; I think Finland has one; I suspect Germany has one. Closer to home, for me, at least, France has one. Now, those who read my blogging know that I am not especially pro-French or pro-France. But I can testify to a fair extent that the French National Healthcare works well. I have used it several times across the past fifty years. I have observed it closely on the occasion of my mother’s slow death.
The French national health system is friendly, almost leisurely, and prompt in giving you appointments including to specialists. It tends to be very thorough to the point of excessive generosity, perhaps. Yes, but you get what you pay for, I can hear you thinking – just like a chronically pessimistic liberal would. Well, actually, Frenchmen live at least three years longer on the average than do American men. And French women live even longer. (About the same as Canadians, incidentally.)
Now, the underlying reasoning is a bit tricky here. I am not stating that French people live longer than Americans because the French national healthcare delivery system is so superior. I am telling you that whatever may be wrong with the French system that escaped my attention is not so bad that it prevents the French from enjoying superior longevity. I don’t want to get here into esoteric considerations of the French lifestyle. And, no, I don’t believe it’s the red wine. The link between drinking red wine daily and cardiac good health is in the same category as Sasquatch: I dearly hope it exists but I am pretty sure it does not. So, I just wish to let you know that I am not crediting French health care out of turn.
The weak side of the French system is that it remunerates doctors rather poorly, from what I hear. I doubt French pediatricians earn $222,000 on the average. (Figure for American pediatricians according to the Wall Street Journal 8/17/18.) But I believe in market processes. France the country has zero trouble finding qualified candidates for its medical schools. (I sure hope none of my current doctors, whom I like without exception, will read this. The wrong pill can so easily happen!)
By the way, I almost forgot to tell you. Total French health care expenditure per person is only about half as high as the American. Rule of thumb: Everything is cheaper in the US than in other developed countries, except health care.
And then, closer to home, there is a government health program that covers (incompletely) about 55 million Americans. It’s not really “universal” even for the age group it targets because one must have contributed to benefit. (Same in France, by the way, at least in principle.) It’s universal in the sense that everyone over 65 who has contributed qualifies. It’s not a charity endeavor. Medicare often slips the minds of critical American conservatives, I suspect, I am guessing, because there are few complaints about it.
That’s unlike the case for another federal health program, for example the Veterans’, which is scandal-ridden and badly run. It’s also unlike Medicaid, which has the reputation of being rife with financial abuse. It’s unlike the federally run Indian Health Service that is on the verge of being closed for systemic incompetence.
I suspect Medicare works well because of a large number of watchful beneficiaries who belong to the age group in which people vote a great deal. My wife and I are both on Medicare. We wish it would cover us 100%, although we are both conservatives, of course! Other than that, we have no complaints at all.
Sorry for the seeming betrayal, fellow conservatives! Is this a call for universal federal health care in America? It’s not, for two reasons. First, every country with a good national health system also has an excellent national civil service, France, in particular. I have no confidence, less than ever in 2018, that the US can achieve the level of civil service quality required. (Less in 2018 because of impressive evidence of corruption in the FBI and in the Justice Department, after the Internal Revenue Service).
Secondly, when small government conservatives (a redundancy, I know) attempt to promote their ideas for good government primarily on the basis of practical considerations, they almost always fail. Ours is a political and a moral posture. We must first present our preferences accordingly rather than appeal to practicality. We should not adopt a system of health delivery that will, in ten years, attribute the management of 13% of our national income to the federal government because it’s not infinitely trustworthy. We cannot encourage the creation of a huge category of new federal serfs (especially of well-paid serfs) who are likely forever to constitute a pro-government party. We cannot, however indirectly, give the government most removed from us, a right of life and death without due process.
That simple. Arguing this position looks like heavy lifting, I know, but look at the alternative.
PS I like George Mason University, a high ranking institution of higher learning that gives a rare home to conservative American scholars, and I like its Mercatus Center that keeps producing high-level research that is also practical.
Nightcap
- Reclaiming Full-Throttle Luxury Space Communism Aaron Winslow, Los Angeles Review of Books
- Elves and Aliens Nick Richardson, London Review of Books
- Imperialism, American-style Michael Auslin, Claremont Review of Books
- The Congo reform project: Too dark altogether Angus Mitchell, Dublin Review of Books
Eye Candy: travel advice for Dutch citizens
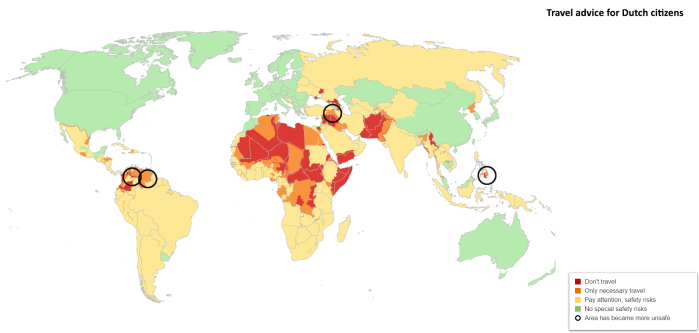
Interesting map, for a few reasons. The United States is in green, which means there are “no special safety risks” to worry about. What I take this to mean is that as long as you stay out of, say, North Sacramento, or East Austin, when the sun goes down you’ll be safe.
The “pay attention, safety risks” label makes quite a big jump in my conceptual understanding of this map. What this warning means is that if you are particularly stupid, you won’t end up getting mugged and losing your wallet (like you would in green areas), you will instead end up losing your life or being kidnapped for ransom (or slavery).
This is quite a big jump, but it makes perfect sense, especially if you think about the jump in terms of inequality and, more abstractly, freedom.
Nightcap
- The return of Henry George Pierre Lemieux, EconLog
- The politics of purity and indigenous rights Grant Havers, Law & Liberty
- The Ottoman Empire’s first map of the United States Nick Danforth, the Vault
- The age that women have babies: how a gap divides America Bui & Miller, the Upshot
Nightcap
- Death of a Marxist Vijay Prashad, The Hindu
- We’re on the threshold of a third wave of globalization. What should we expect? Branko Milanovic, globalinequality
- Turkey kills PKK’s leader in Iraq Amberin Zaman, Al-Monitor
- France’s second-class citizens Haythem Guesmi, Africa is a Country
Naipaul (RIP) and the Left
The most interesting reflection on V.S. Naipaul, the Nobel Prize winner who died earlier this week, comes from Slate, a low-brow leftist publication that I sometimes peruse for book reviews. Naipaul, a Trinidadian, became loathed on the left for daring to say “what the whites want to say but dare not.”
The fact that Slate‘s author tries his hardest to piss on Naipaul’s grave is not what’s interesting about the piece, though. What’s interesting is what Naipaul’s wife, a Pakistani national and former journalist, has to say about Pakistan:
[…] she smiled and asked if I knew what Pakistan needed. I informed her that I did not. “A dictator,” she replied. At this her husband laughed.
“I think they have tried that,” I said, doing my best to stay stoic.
“No, no, a very brutal dictator,” she answered. I told her they had tried that, too. “No, no,” she answered again. Only when a real dictator came in and killed the religious people in the country, and enough of them that the streets would “run with blood,” could Pakistan be reborn. It was as if she was parodying a gross caricature of Naipaul’s worst views—and also misunderstanding his pessimism about the ability of colonial societies to reinvent themselves, even through violence—but he smiled with delight as she spoke.
“That’s so American of you,” she then blurted out, before I had said anything. My face, while she had been talking, must have taken on a look of shock or disgust. “You tell a nice young American boy like yourself that a country needs a brutal dictator and they get a moralistic or concerned look on their face, as if every country is ready for a democracy. They aren’t.”
Damn. This testy exchange highlights well what the developing world is facing, intellectually. Religious conservatives heavily populate developing countries. Liberals, on the left and on the right, in developing countries are miniscule in number, and most of them prefer, or were forced, to live in exile. Liberty is their highest priority, but the highest priority of Western elites, whose support developing world liberals’ desperately need, is democracy, which empowers a populace that cares not for freedom.
So what you get in the developing world is two kinds of autocracies: geopolitically important autocracies (like Pakistan), and geopolitically unimportant autocracies (think of sub-Saharan Africa).
That Naipaul and his wife had the balls to say this, for years, is a testament to the magnificence of human freedom; that Leftists have loathed Naipaul for years because he had pointed this out is a bitter reminder of why I left the Left in the first place.
By the way, here is Naipaul writing about the GOP for the New Yorker in 1984. And here is my actual favorite piece about Naipaul.
10 horrific ways to die (RCH)
Yes, that’s the subject of my weekend column over at RealClearHistory. An excerpt:
4. Cutting off limbs/flaying. The English version of being hanged, drawn, and quartered involved removing genitals, but did any other society in history stoop so low? Um, yes. Not only have penises and/or testicles been removed and vaginas flayed, but they have sometimes been displayed as trophies, eaten, or converted into jewelry. Genitals aren’t the only limbs to have been removed over the years. Fingers and toes, tongues, breasts, eyes, ears, lips, nipples, noses, kneecaps, fingernails, eyelids, skin, and bones have all been forcibly removed over years by governments exacting punishment. Aside from the removal of genitals, flaying is probably the worst of the bunch. That’s when you beat somebody so hard that their skin comes off.
I had a lot of fun writing this, and I suspect my ever-so-patient editor had a lot of fun reading (and editing) it. I hope you enjoy it too! Here’s the rest of it.
Nightcap
- World War II and the point of Surrealism Sophie Haigney, 1843
- Is religion a universal in human culture? Brett Colasacco, Aeon
- Sikh pilgrimages: Hope for a religious corridor Tridivesh Singh Maini, The News
- For centuries, people thought lambs grew on trees Abbey Perreault, Atlas Obscura
Nightcap
- End the double standards in reporting political violence David French, National Review
- Campaign politics and the origins of the Vietnam War Rick Brownell, Historiat
- Hussein Ibish on Muslim identity Irfan Khawaja, Policy of Truth
- Friends of freedom and Atlantic democratization Micah Alpaugh, Age of Revolutions