- Sexual Harassment’s Legal Maze Rachel Lu, Law & Liberty
- Why the argument for democracy may finally be working for socialists rather than against them Corey Robin, Crooked Timber
- How much value does the Chinese government place on freedom? Scott Sumner, EconLog
- Authoritarian Nostalgia Among Iraqi Youth Marsin Alshamary, War on the Rocks
China
Eye Candy: Shanghai Cooperation Organization
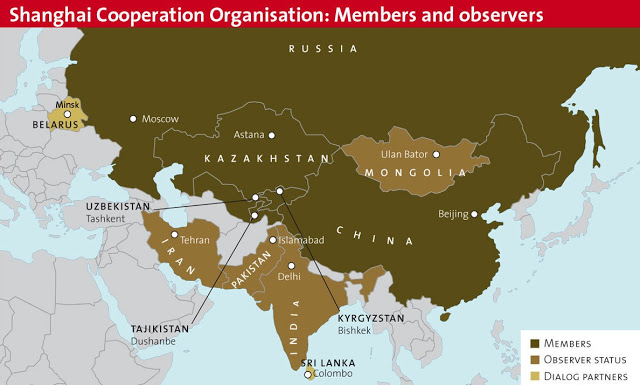
First off, Shanghai and Warsaw are two very different cities, and because of that I think the SCO is a different animal than the Warsaw Pact. For one thing (aside from the difference in the two cities, one being selected for its geographical prominence, the other for its commercial acumen), the Warsaw Pact was a military alliance led by the Soviet Union, while the SCO is dedicated to political and economic cooperation as well as military security. Notably, the security aspect of the SCO is dedicated to coordinating state-led efforts against terrorism and separatism rather than against a rival alliance.
I don’t see anything wrong with multilateral efforts undertaken by states other than the US. I don’t see any need to worry, fret, or otherwise suspect the SCO of undermining world peace and prosperity. The fact that the SCO is made up of cooperating autocratic regimes rather than democratic ones does not faze me. The SCO has been making overtures to the democracies of India, Iran, and Sri Lanka (be sure to check out Tridivesh’s excellent take on India and the SCO), and multilateral cooperation among states is in itself an exercise in political participation among equals, albeit not at an individual level.
There is also cause to be happy that China and Russia have bound themselves up in such a prominent cooperative venture, too, given the two powers’ history of fighting each other. The SCO is contributing to peace and prosperity, and while it appears on the surface that the venture is designed to be a rival of the Western-built world order, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization actually contributes to it.
(h/t Nick)
Nightcap
- Did Cicero Devise Modern Constitutional Thought on His Own? David Potter, Law & Liberty
- Russia’s Pacific history is little known, perhaps even in Russia Peter Gordon, Asian Review of Books
- The Opium War and the Humiliation of China Ian Morris, New York Times
- The Puzzle of Russian Behavior in Deir al-Zour Kimberly Marten, War on the Rocks
Could free speech have led to overseas empires?
Tridivesh’s recent post on China’s multilateral struggles got me thinking about the difference between the United States and China when it comes to coalition-building and international affairs more broadly.
I don’t think the Chinese are purposely attempting to smaller countries in debt so that Beijing may have a shorter leash for them. I think Beijing simply doesn’t know what it’s doing, and is proceeding apace with multilateral initiatives like the BRI through a trial-and-error process. Unfortunately, trial-and-error processes only work if there is a mechanism to identify the error that takes place during the trial. In the West, we call this mechanism “free speech.” In China, free speech ruins order and is thus discouraged at best and disposed of at worst.
China’s expansionist efforts will probably, as a result of the lack of free speech, end poorly for the regime. Beijing’s reputation will suffer, and it will have to resort to more coercive tactics to secure its alliances and influence over its smaller neighbors.
This thought process, in turn, got me thinking about how the West came to churn out so many powerful worldwide empires in such a short span of time, and how these empires managed to coexist with each other at various points in time. Given China’s troubles with establishing hegemony, the fact that the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, France, and the United States were able to achieve what they achieved is amazing. Throughout most of history, empires (or wanna-be empires) have sought to expand abroad while keeping order at home, just like China is doing today. In the sixteenth-century West, order at home was rejected in favor of liberty at home, and as a result the few societies that tried liberty ended up being able to afford overseas empires, where order was sought instead of liberty!
The short-sightedness of imperialists continues to astound me. If liberty at home leads to opportunities to establish colonies abroad, why on earth would you try to stamp out liberty in the colonies you’ve been able to establish thanks to liberty? Imagine if the people living in Indonesia, or India, or Algeria, or the Philippines, had all the liberty that Americans and western Europeans had. Alas…
Nightcap
- How cotton unraveled the Chinese patriarchy Melanie Meng Xue, Aeon
- Trump, conservatives, and human rights Seth Kaplan, American Affairs
- On paper, federations generally seem like a good idea Emiliano Travieso, Decompressing History
- Switzerland’s mysterious fourth language Dena Roché, BBC
Hegemony is hard to do: China, globalization, and “debt traps”
As a result of an increasingly insular United States, with US President Donald Trump’s imposition of tariffs, China has been trying to find common cause with a number of countries, including US allies such as Japan, India and South Korea, on the issue of globalization.
While unequivocally batting in favor of an open economic world order, Chinese President Xi Jinping has also used forums like Boao to speak about the relevance of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) (also known as the One Belt and One Road Initiative, or OBOR). At the Boao Forum (April 2018), the Chinese President sought to dispel apprehensions with regard to suspected Chinese aspirations for hegemony:
China has no geopolitical calculations, seeks no exclusionary blocs and imposes no business deals on others.
There is absolutely no doubt that the BRI is a very ambitious project, and while it is likely to face numerous obstacles, it is a bit naïve to be dismissive of the project.
Debt Trap and China’s denial
Yet China, in promoting the BRI, is in denial with regard to one of the major problems of the project: the increasing concerns of participant countries about their increasing external debts resulting from China’s financial assistance. This phenomena has been dubbed as a ‘debt trap’. Chinese denialism is evident from an article in the English-language Chinese daily Global Times titled ‘Smaller economies can use Belt and Road Initiative as leverage to attract investment’. The article is dismissive of the argument that BRI has resulted in a debt trap:
It is a misunderstanding to worry that China’s B&R initiative may elevate debt risks in nations involved in massive infrastructure projects. Countries are queuing up to cooperate with China on its B&R initiative, but many Western observers claim the initiative will create a problem of debt sustainability in countries and regions along the routes, especially those with small economies.
The article begins by citing the example of Djibouti in Africa, and how infrastructure projects are generating jobs and also helping in local state-capacity building. It then cites other examples, like that of Myanmar, to put forward the point that accusations against Beijing of promoting exploitative economic relationships with participant countries in the BRI is far from the truth.
The article in Global Times conveniently quotes Myanmar’s union minister and security adviser, Thaung Tun, where he dubbed the Kyaukpu project a win-win deal, but it conveniently overlooked the interview of Planning and Finance Minister, Soe Win, who was skeptical with regard to the project. Said Soe Win in an interview with Nikkei:
[…] lessons that we learned from our neighboring countries, that overinvestment is not good sometimes.
Soe Win also drew attention to the need for projects to be feasible, and for the need to keep an eye on external debt (Myanmar’s external debt is nearly $10 billion, and 40 percent of this is due to China).
The case of Sri Lanka, where the strategically important Hambantota Port has been provided on lease to China (for 99 years) in order to repay debts, is too well known.
The new government in Malaysia, headed by Mahathir Mohammed, has put a halt on three projects estimated at over $22 billion. This includes the $20 billion East Coast Railway Link (ECRL), which seeks to connect the South China Sea (off the east coast of peninsular Malaysia) with the strategically important shipping routes of the Straits of Malacca to the West. A Chinese company, China Communications Construction Co Ltd, had been contracted to build 530km stretch of the ECRL. On July 5, 2018 it stated that it had suspended work temporarily on the project, on the request of Malaysia Rail Link Sdn Bhd.
The other two projects are a petroleum pipeline spread 600km along the west coast of peninsular Malaysia, and a 662km gas pipeline in Sabah, the Malaysian province on the island of Borneo.
During a visit to Japan, Mahathir had categorically said that he would like to have good relations with, but not be indebted to, China, and would look at other alternatives. The Malaysian PM shall also be visiting China in August 2018 to discuss these projects.
Conclusion
While Beijing has full right to promote its strategic interests, and also highlight the scale and relevance of the BRI, it needs to be more honest with regard to the issue of the ‘debt trap’ (especially if it claims to understand the sensitivities of other countries, and does not want to appear to be patronizing). While smaller countries may be economically dependent upon China, the latter should dismiss the growing resentment against some of its projects at its own peril. Countries like Japan have already sensed the growing ire against the Chinese, and have begun to step in, even in countries like Cambodia (considered close to China). A number of analysts are quick to state that there is no alternative to Chinese investment, but the worries in smaller countries with regard to Chinese debts proves the point that this is not the case. China needs to be more honest, at least, in recognizing some of its shortcomings in its dealings with other countries.
Nightcap
- The illiberal conception of freedom Nick Nielsen, The View from Oregon
- The echoes of Chinese exclusion (immigration) Irene Hsu, New Republic
- The Middle Kingdom: all under heaven? George Walden, American Interest
- Have we forgotten how to die? Julie-Marie Strange, Times Literary Supplement
A note on India’s performance at the recent SCO Summit
The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Summit, from June 9-10, went largely as expected. The Indian Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, met the Chinese President, Xi Jinping, on the sidelines of the summit. New Delhi’s proposal to have an informal summit, in India in 2019, on the lines of the Wuhan Summit (held in April 2018) was accepted by the Chinese. Agreements were also signed between both countries with regard to sharing hydrological data on the Brahmaputra River, and export of non-Basmati varieties of rice from India. Another issue, which was discussed during the Modi-Xi meeting, was the joint capacity development project in Afghanistan, which was first proposed during the Wuhan Summit.
Commenting on his meeting with the Chinese President, Modi tweeted:
Met this year’s SCO host, President Xi Jinping this evening. We had detailed discussions on bilateral and global issues. Our talks will add further vigour to the India-China friendship.
Modi’s meetings with leaders of other member countries
The Indian PM met other leaders of member countries, including the presidents of Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. While there was no formal meeting with the Pakistani President Mamnoon Hussain, Modi did shake hands with Hussain and exchange pleasantries. Interestingly, Chinese President Xi Jinping, during his address, had spoken about the presence of both leaders, as well as entry of both countries into the SCO. Said the Chinese President: Continue reading
Nightcap
- The rule of robots in Stiglitz and Marx Branko Milanovic, globalinequality
- Freud and property rights Bill Rein, NOL
- China at its limits: beyond its borders Joshua Bird, Asian Review of Books
- Who’s Afraid of Tribalism Blake Smith, Quillette
The great global trend for the equality of well-being since 1900
Some years ago, I read The Improving State of the World: Why We’re Living Longer, Healthier, More Comfortable Lives on a Cleaner Planet by Indur Goklany. It was my first exposition to the claim that, globally, there has been a long-trend in the equality of well-being. The observation made by Goklany which had a dramatic effect on me was that many countries who were, at the time of his writing, as rich (incomes per capita) as Britain in 1850 had life expectancy and infant mortality levels well superior to 1850 Britain. Ever since, I accumulated the statistics on that regard and I often tell my students that when comes the time to “dispell” myths regarding the improvement in living standards since circa 1800 (note: people are generally unable to properly grasp the actual improvement in living standards).
Some years after, I discovered the work of Leandro Prados de la Escosura who is a cliometrician who (I think I told him that when I met him) influenced me deeply in my work regarding the measurement of living standards and who wrote this paper which I will discuss here. His paper, and his work in general, shows that globally the inequality in incomes has faltered since the 1970s. That is largely the result of the economic rise of India and China (the world’s two largest antipoverty programs). 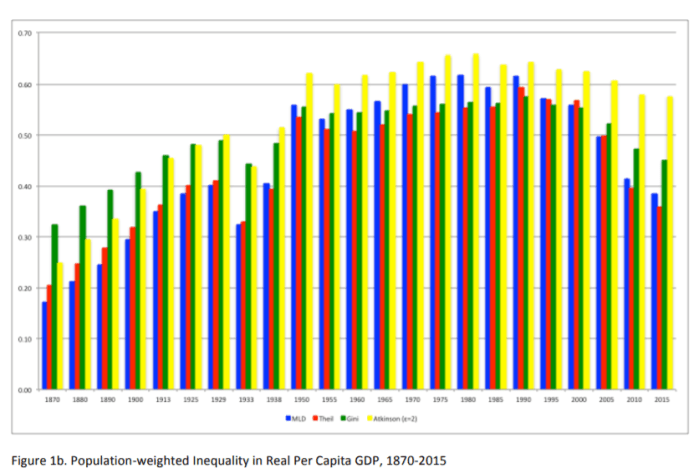
However, when extending his measurements to include life expectancy and schooling in order to capture “human development” (the idea that development is not only about incomes but the ability to exercise agency – i.e. the acquisition of positive liberty), the collapse in “human development” inequality (i.e. well-being) precedes by many decades the reduction in global income inequality. Indeed, the collapse started around 1900, not 1970!
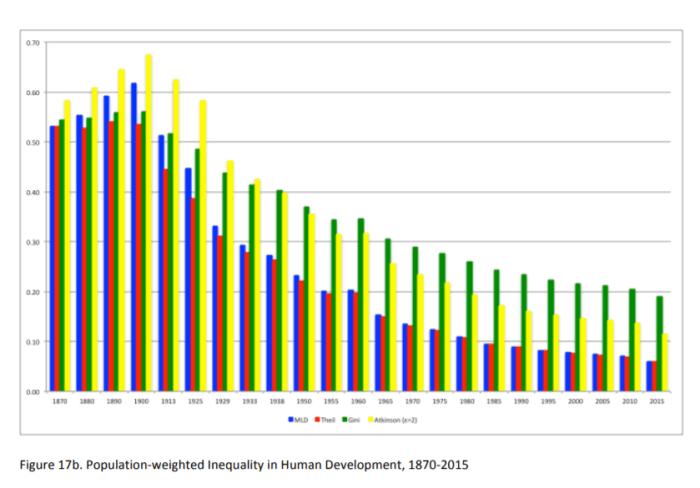
In reading Leandro’s paper, I remembered the work of Goklany which had sowed the seeds of this idea in my idea. Nearly a decade after reading Goklany’s work well after I fully accepted this fact as valid, I remain stunned by its implications. You should too.
Nightcap
- Antarctica’s long, dark winter Sarah Laskow, Atlas Obscura
- The worst volcanic eruption in US history Rick Brownell, Historiat
- Aftershocks from the 2008 Sichuan earthquake Ian Johnson, NY Review of Books
- Put the “human” back into human capital Parag Khanna, Strait Times
The Indo-Pacific narrative, US insularity, and China’s increasing influence
Over the past year, there has been a growing interest with regard to the vision of a Free and Fair ‘Indo-Pacific’. While this term has been used in recent years by policy makers from the US and Australia and has been pushed forward by a number of strategic analysts, a number of developments since last year have resulted in this narrative gaining some sort of traction.
US President Donald Trump, during his visit to South East Asia and East Asia in November 2017, used this term on more than one occasion, much to the discomfort of China (which prefers ‘Asia-Pacific’). On the eve of his visit to India last year, Former Secretary of State Richard Tillerson, while speaking at the Centre for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS, Washington DC), explicitly mentioned a larger role for India in the Indo-Pacific, and the need for India and US to work jointly. Said Tillerson:
The world’s center of gravity is shifting to the heart of the Indo-Pacific. The U.S. and India, with our shared goals of peace, security, freedom of navigation, and a free and open architecture, must serve as the Eastern and Western beacons of the Indo-Pacific, as the port and starboard lights between which the region can reach its greatest and best potential.
In November 2017, the Quad grouping (Australia, US, India, and Japan) met on the sidelines of the ASEAN Summit pitching not just for a rules based order, but also in favour of enhancing connectivity. Commenting on the meeting, an official statement from the US Department of State had said that the discussions were important and members of the Quad were “committed to deepening cooperation, which rests on a foundation of shared democratic values and principles.”
Earlier, too, the four countries had coalesced together, but as a consequence of Chinese pressure, the grouping could not last.
There have also been discussions of coming up with connectivity projects. This was discussed during Australian Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull’s meeting with Donald Trump in February 2018, and between representatives of Japan, the US, and India in April 2018 when the three sides met in New Delhi, committing themselves to furthering connectivity between the countries.
China Factor
While members of the Quad have continuously denied that the Indo-Pacific concept is specifically targeted at China, it would be naïve to believe this assertion. In fact, during a visit to Australia, French President Emmanuel Macron, who is trying to position himself as one of the frontline protagonists of liberalism in the Western world, spoke about the need for India, Australia, and France to work together in order to ensure a rules-based order. Commenting on the need for India, France and Australia to jointly work for a rules based order, and checking hegemony (alluding to China), the French President stated:
What’s important is to preserve rules-based development in the region… and to preserve necessary balances in the region….It’s important with this new context not to have any hegemony.
Evolving relationship between China-India and China-Japan
While it is good to talk about a rules-based order, and a Free and Fair Indo-Pacific, it is important for members to do a rational appraisal of ensuring that the Indo-Pacific narrative remains relevant, especially in the context of two important events. First, the reset taking place between India-China, and second, the thaw between Japan-China.
This has already resulted in some very interesting developments.
First, Australia was kept out of the Malabar exercises last June (Japan, US, and India participated). Australia is a member of the Quad alliance and has been one of the vocal protagonists of the Free and Fair Indo-Pacific narrative. Canberra has also expressed vocally the need for a greater role for India in the Indo-Pacific. Australia has on more than one occasion expressed its desire to participate in the Malabar Exercises.
Many argue that the decision to exclude Australia from the exercises is a consequence of the significant shift taking place in India-China relations, though India has been dismissive of this argument.
Second, Japan has expressed its openness to participate in China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) as long as international norms are met. During meetings between the Chinese and Japanese Foreign Ministers in April 2018, the Chinese Foreign Minister, Wang Yi, said such a possibility was discussed. Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, who is seeking to improve ties with China, recently reiterated the potential of the Belt and Road Initiative in giving a boost to the regional economy.
It would be pertinent to point out that a number of Japanese companies are already participating in countries which are part of the Belt and Road Initiative.
Interestingly, the Japanese-led Asian Development Bank (ADB), which has been funding many projects (spearheaded by Japan) projected to be components of the Indo-Pacific strategy, has even gone to the extent of stating that it does not perceive the Chinese-led Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) as a threat. Commenting on the possibility of cooperation between ADB and AIIB, the President of ADB, Takehiko Nakao, stated that “AIIB, it’s not the kind of threat to us. We can cooperate with AIIB because we need larger investment in Asia and we can collaborate.”
Where does the Indo-Pacific move from here?
In terms of strategic issues, especially ensuring that China is not an unfettered influence in the region, the narrative is relevant. The Chinese approach towards Indo-Pacific and Quad as being mere froth is an exaggeration. Addressing a press conference on the sidelines of the National People’s Congress, China’s Foreign Minister, Mr. Wang, had stated that there was “no shortage of headline grabbing ideas” but they were “like the foam on the sea” that “gets attention but will soon dissipate.”
Similarly, in terms of promoting democratic values it certainly makes sense. The real problem is in terms of connectivity projects (beyond India-Japan, none of the members of the Quad have elaborated a coherent vision for connectivity). The US has spoken about an Indo-Pacific Economic Corridor, but given the Trump Administration’s approach, it remains to be seen to what extent this can be taken further. While Australia has been steadfast in its opposition to China’s growing economic clout, it has its limitations, especially in terms of funding any concrete connectivity projects. Possible regions where Australia could play a key role should be identified.
Conclusion
It is fine to speak in terms of certain common values, but to assume that China can be the only glue is a bit of a stretch, especially given the fact that it has strong economic ties with key countries pushing ahead the Indo-Pacific vision. It is also important for the Indo-Pacific to come up with a cohesive connectivity plan. Currently, the narrative seems to be driven excessively by strong bilateral relationships, and the individual vision of leaders.
Beijing and the India-Pakistan conundrum
During the course of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) meeting in China, and days before Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi arrived in China for his summit with Chinese President Xi Jinping, an editorial in Pakistan’s premier English-language daily (Daily Times) titled ‘China’s re-assurance on CPEC‘ made an interesting point:
If anything Beijing has been asking Islamabad to engage with New Delhi and keep tensions to a minimum. Such an environment is also conducive to timely completion of various projects under CPEC [China-Pakistan Economic Corridor] and transforming South and Western Asia into a high economic growth zone. Keeping the economy first is a lesson that our state has yet to learn from its big brother in the hood.
Zardari’s recommendation in 2012
Interestingly, during his meeting with former Indian Prime Minister Dr Manmohan Singh, in April 2012, former Pakistan President Asif Ali Zardari (Pakistan People’s Party — PPP) had also stated that Pakistan and India should seek to follow the Pakistan-China model of engagement. Zardari meant that, like India and China, India and Pakistan too should follow an incremental approach, with more frequent high level interactions and a heavy focus on economic cooperation.
It might be mentioned that between 2012 and 2013 some important leaps were made in the economic sphere between both countries, with the most noteworthy development being the setting up of the Integrated Check Post (ICP) at Attari (Amritsar, India). The ICP’s motive was to accelerate bilateral trade through the only land crossing (Attari-Wagah) between India and Pakistan. During this period, a number of high level delegations interacted, including the Commerce Ministers of both countries.
Pakistan also seemed prepared to grant India MFN status, but a change of government (along with domestic opposition from certain business lobbies as well as hardliners) in Islamabad (2013) and then New Delhi (2014) meant that this decision could not go ahead. Since then, relations have been tense, and there has been no opportunity to make any progress on this.
Tensions in the past 4 years: CPEC and terrorism emanating from Pakistan Continue reading
Bolton’s Iran policy: could it strengthen the China-Russia-Iran-Pakistan axis?
John Bolton, who took over as Donald Trump’s National Security Adviser on April 8, has had significant differences with India on a number of issues in the past. As US Ambassador to the UN, he opposed India’s elevation to the United National Security Council (UNSC), even at a time when relations were at a high during the Manmohan Singh-Bush era. Bolton had initially opposed the Indo-US nuclear deal, though later he lent his support. While the Trump administration has sought to elevate India’s role in the Indo-Pacific region, Bolton has expressed the view that there are some fundamental differences between India and the US. In the short term, though, there is no serious divergence.
Bolton and Iran
What would really be of concern to India however is Bolton’s hawkish approach towards Iran. Bolton’s views are not very different from those of US President Donald Trump and recently appointed Secretary of State John Pompeo. Bolton is opposed to the Iran Nuclear Agreement signed between Iran and P5+1 countries in 2015. In 2015, the NSA designate called for bombing Iran, last year he had criticized the deal, and last year he had called for scrapping the deal.
The Iranian response to Bolton’s appointment was understandably skeptical. Commenting on Bolton’s appointment, Hossein Naghavi Hosseini, the spokesman for the Iranian parliament’s National Security and Foreign Policy Commission, said: Continue reading
Recent developments in the context of Indo-Pacific
At a time when a massive churn is taking place in the Donald Trump Administration (HR Mcmaster was replaced as head of the NSA by John Bolton, while Secretary of State Rex Tillerson was replaced with the more hawkish Mike Pompeo), Alex Wong, Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for East Asian and Pacific Affairs, gave a briefing with regard to the US vision for ‘Indo-Pacific’ strategy, on April 3, 2018 (a day before a trilateral dialogue took place between senior officials from India, Japan and US). Wong outlined the contours of the strategy, and spoke not just about the strategic vision, but also the economic vision of the US, with regard to the Indo-Pacific.
A backgrounder to the Indo-Pacific, Quad, and the China Factor
For a long time, the US referred to the region as ‘Asia-Pacific’ (which China prefers), but the current Trump Administration has been using the term ‘Indo-Pacific’. During his visit to East Asia and South East Asia, in November 2017, the US President had used the term more than once (much to the discomfort of China) giving a brief overview of what he meant by a ‘Free and Fair Indo-Pacific’. While speaking to a business delegation at Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Trump spoke about ‘rule of law’ and playing by the rules. Former Secretary of State Rex Tillerson had referred to the Indo-Pacific and the Quad Alliance (consisting of US, India, Japan, and Australia) in an address at the Center for Strategic and International Studies (a Washington think tank) in October 2017, a week before his India visit.
In order to give a further thrust to the Quad, representatives of all four countries met on the eve of East Asia Summit in Manila. A statement of the Indian Foreign Ministry said: Continue reading