- Fantastic 1947 essay on world federalism under the US constitution (pdf)
- Greater Poland Ethnographic Park
- The tragedy of Stafford Beer (cybersocialism) Kevin Munger, Crooked Timber
- Democracy or liberalism for the Middle East? Jonathan Dean, Law & Liberty
federation
Africa’s quest for sovereignty
That’s the title of this excellent piece by Toby Green, a historian at King’s College London. Green does a wonderful job of highlighting all of the problems that African societies face today: corruption, poverty, and my personal favorite, “neoliberalism.” Neoliberalism is just shorthand for loans that Western financial institutions give to African states. These loans are usually only given if African states promise to follow certain guidelines that Western financial institutions have drawn up. The end result is corruption and poverty.
I can agree that it’s a terrible system, even if I think the name Green has given it is dumb.
Throughout the piece, Green makes a good case for fundamental change in Africa. The problem is that he mistakenly thinks that this change can occur via the states that are currently in place in Africa. He mistakenly thinks that Ghana, Nigeria, Uganda, or Angola, to name some of the more prominent examples, have what it takes to enact the changes necessary for a fundamental shift.
Green argues that “unipolar American and Western European hegemony” (which by definition cannot be unipolar if there’s two poles, unless…) is responsible for Africa’s problems, and that the continent’s early independence leaders should be looked to for guidance. The problem with this, as Hendrik Spruyt has pointed out, is that the continent’s early independence leaders didn’t listen to anybody but themselves. They simply sought to graft their visions of what Africa should be onto the existing colonial governance system of the various European powers.
These early independence leaders sought to forge nations out of the colonies that the Europeans had haphazardly patched together. There were other elites on the African continent who wanted something different from what Africa’s early independence leaders wanted. Some of these elites were nationalists who wanted their states to be fully recognized equals on the world stage, just like the early independence leaders. The difference between these nationalists, and the early independence leaders, was that they wanted to abolish colonial boundaries and restore pre-colonial boundaries which would then be recognized as states within the Westphalian states-system. Like so:
| Early Independence Leaders | Other, actual Nationalists |
| Wanted African states to inherit colonial boundaries | Wanted African states to abolish colonial boundaries and restore old ones to prominence |
| Wanted to create and forge national identities out of these colonial boundaries | Wanted to harness the power of already-existing national identities by tying them to internationally-recognized states |
The early independence leaders obviously won out. The borders of European colonialism were maintained and enshrined within the Westphalian states-system that soon encompassed the globe.
Green and other Leftists think that the above column on the left is a perfectly acceptable way to continue, and that the problem is not the states-system that Africa’s early independence leaders established, but rather the “unipolar hegemony of America and Europe.” Without a rethink of the fundamentals, Green and other Leftists are going to continue inadvertently contributing to the immiseration of Africa.
Don’t get me wrong! The current loan system is awful. It’s terrible. But it’s exactly what you’d expect to get from an order like the one outlined above.
If people are serious about unleashing Africa then they need to look to the above column on the right. The map of the nations that were ignored by Africa’s early independence leaders (ignored, and eventually slaughtered, oppressed, persecuted, and imprisoned) is still there. You can find good maps of nations in Africa — often condescendingly referred to as “ethnic groups” rather than nations – that are superimposed on the map of African postcolonial states. Here’s the best one in the world at the moment.
Green implicitly recognizes that there’s something wrong with the postcolonial African state of Africa’s early independence leaders. He can tell that the column on the left is somehow off:
[…] in many African countries, traditional chiefs [are] more respected than elected officials […] A more damning indictment of the failings of the democratic model promoted across Africa […] is hard to find.
What he can’t seem to do is see that the column on the right lines up almost perfectly with the views that Africans have of their chiefs. Now, the chiefs are by no means revered by everybody in Africa, and there is a strong, if minute, anti-chief current throughout the continent because not everybody wants an Africa based on the tenets of nationalism. The columns above only highlight two strains of thought on how Africa should be governed. There are others, most notably Islamist proposals, but the one that libertarians (and, indeed, most Leftists) should find most attractive is that of the African federalists.
African federalists competed with the two nationalist camps when it became apparent that things were about to change vis-à-vis Africa’s relationship with Europe. While the nationalists embraced decolonization, which meant independence from European colonial rule, the federalists embraced integration with their colonizers. They argued that African colonies could, and should, federate with European countries. This federation would mean that African provinces would stand on equal footing with older provinces of European states. African provinces would be able to practice self-government without resorting to autarky. Like so:
| Early Independence Leaders | Other, actual Nationalists | Federalists |
| Wanted African states to inherit colonial boundaries | Wanted African states to abolish colonial boundaries and restore old ones to prominence | Wanted African colonies to become represented provinces in federated European polities |
| Wanted to create and forge national identities out of these colonial boundaries | Wanted to harness the power of already-existing national identities by tying them to internationally-recognized states | Wanted full citizenship rights within the federated polities that would replace the old European empires |
In hindsight, the federalists were right to deplore the idea of independence from Europe. The Westphalian nation-state, at least as it was envisioned by Africa’s early independence leaders, has been a disaster for Africa. It’s also clear that the federalists had an uphill climb, not only because decolonization-nationalism were all the rage but also because several of the Europeans who ran the colonies did not themselves have federated orders. The French and Portuguese had no experience with federalism, and the Spanish and British had weird federalisms based on monarchical principles. The Dutch and the Americans both had good models to emulate, but they didn’t have any African colonies and the idea of African colonies federating with Dutch or American states was out of the question in the 1960s and 1970s. That doesn’t have to be the case for today.
There’s nothing in this world that says the ideas of Africa’s federalists can’t be put in to practice today. There’s nothing to prevent the world’s most powerful polity, the compound republic of the United States, from entertaining the ideas put forth by Africa’s federalists. Nothing, that is, except the conservatism of Western and Western-educated elites, who believe that Africa’s early independence leaders were somehow right, because even though the results of their actions have gone horribly wrong, their ideals were pure in motive.
Sovereign territory and decolonization movements
But while adopting sovereign territoriality as the dominant script, they were far more cautious in accepting the principle of self-determination for all nationalist claims. While claiming the right of national self-determination as a rhetorical tool in the struggle with the metropolitan powers, they simultaneously denied those claims to indigenous groups within the territorial state that the nationalist leaders envisioned. The Dutch were not incorrect in asserting that the nationalist (Javanese) claim for Indonesian independence subverted the possible independence of many areas and ethnic groups within the East Indies. Sukarno himself of course recognized that “the Dutch had invented Indonesia” given that it had never been a coherent political entity before. [Sukarno] was eager to lay claim to the entire territory as a unified state on the principle of sovereign equality with other states, disregarding local demands for true national self-determination.
This is from the great Hendrik Spruyt, and you can read the whole thing (pdf) here.
I have two takeaways for NOL: first, the people who led decolonization efforts after WWII exploited the maps drawn up by imperial powers; they were not nationalists, they were cosmopolitans who had been educated in European capitals and who had borrowed the logic of nationalists in those capitals. Calls for federation instead of independence/decolonization were few and far between, but they did exist. Adam Smith called for union between the UK and its North American colonies. Several African statesmen called for federation between their lands and France. I believe some Indians called for federation between their land (which included present-day India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh) and the UK, but I need to do more research on this. In Hawaii, the federalists actually won out.
Second, the current narrative, or script as Spruyt calls it, still doesn’t give local/indigenous actors their due. The current Westphalian script — undergirded by the principle of sovereign equality with other states – still treats the leaders of decolonization like victims of imperialism who fought against the odds to defeat intransigent European oppression. There is simply not much being said about the people who called for greater representation within the European imperiums and for federal restructuring of these imperiums.
A third takeaway is that libertarians have a much better alternative to adopt than shallow anti-imperialism, which is just a form of antiwar nationalism: they could call for federation with polities as a foreign policy doctrine. They could actively build alliances with those factions that were squashed by nationalists who disregarded the claims of other groups, with the aim of integrating these societies into a federal order.
Nightcap
- Christian warlords in Iraq and Lebanon Joseph Amar, Commonweal
- The hungry dead and the envoys of Hell Sheng Wenqiang, Sixth Tone
- Why don’t residents of Washington DC have full political rights? Eric Schliesser, D&I
- The Car Ride Mercy Mkhana Simiyu, Jalad
Against Hayek’s globalism
Ignacio, from X, put forth an objection that captures well the spirit of animosity towards worldwide federation under a Hayekian (or, dare I say, Madisonian?) constitutional order:
With Hayek’s globalism we cannot agree: national sovereignties are necessary because:
a) there are different ethnic groups;
b) although free trade does not help to erase deep cultural differences;
c) Where to go into exile if the world were a federation?
I’ve heard these same types of objections over and over again with small minor differences.
Here are some rebuttals, by no means extensive, that may be of interest to those of us who clamor for a much better world.
a) Ethnic groups and national sovereignty don’t go together. In Europe, some ethnic groups have managed to secure for themselves sovereign nation-states, but not without first squashing the rights of other ethnic groups within these territorial borders and forcing the others to become like them. In most of the world outside of Europe, including in the United States, ethnic groups have been incorporated into existing territorially-defined states to varying degrees of success. Some of the ethnic groups, such as Jews in Europe or Palestinians in Israel, have been exterminated, removed, or persecuted harshly, while others have managed to carve out spheres of influence within the existing state’s apparatus of power. These multi-ethnic nation-states are the norm throughout the world, and the world is a lot poorer, a lot more violent, and a lot less free than the United States.
b) It is true that free trade does not erase cultural differences. Free trade doesn’t lead to peace, either. Hayek (and Mises) both recognized these facts, which is why they advocated for a federalist world order to replace the multipolar world from whence they came. Free trade by itself cannot overcome cultural diversity or violence, but free trade coupled with the political, legal, and military integration of two or more polities does squelch cultural chauvinism and intergroup violence. Just ask the Americans.
c) Hayekian globalism doesn’t insist on incorporating every one and everything into its federal world order. Those who want to join, can and should. Those who don’t want to join, don’t have to. Hayekian globalism simply advocates for these policy options to be on the table, and for constitutions to have processes for entrance and exit. Why should Singapore, London, or Tokyo have to federate? Why shouldn’t Malaysia and London-less Britain or Tokyo-less Japan have the option of joining a federation?
Objections to Hayekian globalism and its federal world order are important because they are popular, but that doesn’t make them rooted in fact. The libertarian’s task in our time is to rid our own faction of these pernicious myths, and then go forth boldly and call for a globalism that would actually work.
Nightcap
- Houellebecq’s omelette Theodore Dalrymple, First Things
- Hayek and the Lucas critique David Glasner, Uneasy Money
- An interesting alternative to federation Maxwell Tabarrok, Maximum Progress (h/t Vishnu)
Nightcap
- Federal-republican security versus democratic peace (pdf) Daniel Deudney, EJIR
- Republics in the New World (don’t forget about the Cherokee) John Majewski, TIR
- Fresh air and fascism in the Bavarian Alps Lucy Lethbridge, Spectator
- After Christendom Frederick Christian Bauerschmidt, Commonweal
Nightcap
- “The Philadelphian System: Sovereignty, Arms Control, and Balance of Power in the American States-Union, Circa 1787-1861” (pdf) Daniel Deudney, International Organization
The Federation of Free States: Helping Atlas Shrug
After federating with 51 polities, with one round of peaceful federation happening in 2025 and another in 2045, life in the compound republic got real good, for everyone.
In 2055, diplomats, politicians, and policymakers from the federation began targeting wealthy provinces and countries for membership, a new development that was sparked in part by an alarming rise in despotism (democratic and authoritarian) and in part by stagnant economic growth in the non-Philadelphian interstate order. German, Indian, Brazilian, Italian, and Chinese polities were recruited to join the federation. The Netherlands and the United Arab Emirates were also recruited to join.
The military of the republic is relatively small compared to polities like Russia and China, but far more lethal and technologically advanced, so recruitment was bold. Poaching the rich provinces of second-tier regional powers was not welcomed by the second tiers. They felt bullied. China threatened war, as it did in 2025 when Taiwan joined the federation, but there was nothing the CCP could do about it.
A bunch of separatist regions applied for membership, too. This is probably the most important difference between Westphalian sovereignty and Philadelphian sovereignty. When the Westphalian interstate order was hegemonic, separatists wanted independence; the Philadelphian interstate order gives separatist movements an incentive to join the compound republic instead of trying to go it alone. Westphalian states do not much like the compound republic’s courting of their separatist regions, either.
So between the active courting of wealthy provinces and the active courting of secessionist movements, the stage has been set for a less-than-peaceful round of federating with polities that wish to join the federation of free states.
Many poor states continued to apply for membership, too.
In 2055, here is what the Philadelphian interstate order looks like:

Lagos and Los Angeles joined New York, Tokyo, and London as major financial centers. The people in Canaan, England, and Wales, taking a page out of the Ashanti playbook, let their nationalist sentiments wane to a cultural level rather than a politico-legal level. The people in these “states” had finally come to terms with their place in the Philadelphian interstate order.
The German states of Bavaria, Lower Saxony, North Rhine-Westphalia (how ironic!), Baden-Württemberg, and Rhine-Hesse (a combination of the current states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate) all joined the federation.
The Netherlands joined as is. The Dutch provinces have a long, proud history of republicanism, and it was not an easy choice to make. But by themselves, they were just too small to join the federation, so they banded together a la the Nigerian states of 2045, and joined as a single unit, where they enjoy two Senate seats and roughly the same amount of representatives in Congress as New York or Pennsylvania.
Five Italian provinces joined: Veneto, Lombardy, Trentino-South Tyrol, Piedmont, and Liguria. Piedmont’s membership in the Philadelphian union is all the more remarkable given its role in forming Italy as a nation-state.
The Baltic states and many parts of Poland applied for membership, but the Baltic states could not, in the end, give up their Westphalian sovereignty, and the Polish voivodeships, too small to be admitted on their own, could not come up with a suitable agreement for merging and forming new “states” to join the Philadelphian union.
The United Arab Emirates joined as is.
Three of the wealthiest Indian states joined the federation: Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra. India was upset, but it’s long history of democratic and federal government, along with its close relationship with the West and relative military weakness compared to the union, prevented a war over the three states leaving for the compound republic.
War did not come to China, either, when the federation of free states poached five southern provinces and two special administrative units: Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, Guangxi, and Guangdong (which merged with Macau and Hong Kong). The provinces were in almost open rebellion against the CCP. They had grown tired of the Party’s paranoia and broken promises. Street protests were massive. There is a history of violent uprisings in the region. The CCP, which had turned inward when Taiwan joined the Philadelphian union in 2025, had impoverished the country. Beijing had a massive military but it was outdated, ill-disciplined, and corrupt. China had no means to fight a war over the wealthy provinces that joined the compound republic. Unlike the 19th century, when China was humiliated by the West, only the Communist Party of China was humiliated in this confrontation.
Six of Brazil’s wealthiest states also joined the Philadelphian interstate order: Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais, São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul. Atlas shrugged, and the compound republic responded.
Lebanon gave up its sovereignty, too, but it joined Canaan so no new Senators were added. (I didn’t do the math, but Canaan might or might not get another seat in the House of Representatives.)
Secessionist movements have flowered since the experiment in self-government under the Madisonian constitutional order went global. It’s a counter-intuitive notion: the larger the Philadelphian union gets, the more secessionist movements flourish. In 2055, there were 26 more “states” that joined the compound republic, giving the union 127 members overall.
Hayek the globalist
“Since it has been argued so far that an essentially liberal economic regime is a necessary condition for the success of any interstate federation, it may be added, in conclusion, that the converse is no less true: the abrogation of national sovereignties and the creation of an effective international order of law is a necessary complement and the logical consummation of the liberal program.”
The case for Taiwan’s statehood
When Russia invaded Ukraine a few short weeks ago, some people began to worry that China might try to do the same thing with Taiwan. I didn’t worry about this myself, as China is mostly a paper tiger, but also because the US has close military ties with Taiwan. Taiwan has close economic relationships with several wealthy democratic states in East Asia, too. Contrast this geopolitical context with Ukraine, and the parallels, while tempting, do not add up.
The whole debate and worry over Taiwan got me thinking again about federation as a libertarian foreign policy. Why shouldn’t Taiwan just join the United States? Here are the most common objections to such a federation:
Geography. This is probably one of the strongest cases against Taiwan joining the US, since it’s so far away from not only the mainland but Hawaii, too. Aaaand it’s just off the coast of China, which would likely cause friction with the regional power were Beijing to suddenly find itself neighboring a transoceanic republic.
This is all much ado about nothing. A plane ride from Dallas to Taipei is 14 hours if you take out the layovers. Somebody living in Kaohsiung could send me an email after reading this essay and I could access it within minutes. Geography still matters, but its not an insurmountable barrier to a freer, more open world via the federative principles of the United States constitution.
Culture. A big complaint I see about adding “states” to the American republic is “culture.” Fellow Notewriter Edwin does this all the time, and it can make sense, on the surface, in some cases, but not in Taiwan’s, and not in the Indo-Pacific more generally.
Look at Taiwan’s 2020 presidential election results:
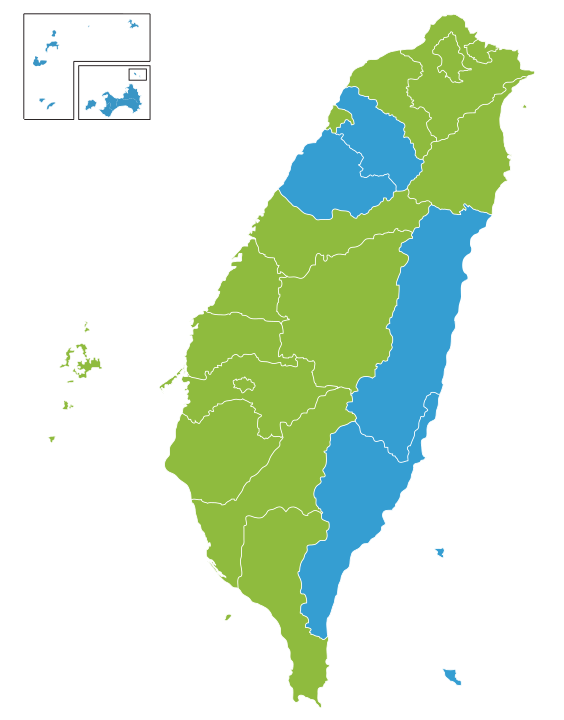
Look familiar? There’s only two colors. It’s a contest between a left-wing and right-wing, and both wings are committed to, and bound by, liberty and democracy. There are no “ethnic” parties, no “religious” parties, and no radical parties, mostly because Taiwan has the same electoral system as the US does: a “first-past-the post” one. So the cultural angle is even weaker than first imagined. Taiwan started out as a nationalist holdout against the Communist Party, but today nationalism doesn’t carry a whole lot of weight. Adding Taiwan to the republic would be like adding another California or Hawaii, albeit with more conservative votes. It’s plausible that adding Taiwan would give Democrats two more reliable seats in the senate, but this is merely cause to invite a polity that would reliably vote Republican to also join the United States.
Self-determination / cultural autonomy. There’s an argument in some circles that joining the US would be akin to losing self-determination and even cultural autonomy. I don’t see how any of this could be true. Even today, people in American states retain a “state-centric” identity when it comes to thinking about their place in the US. That Taiwanese would be able to add “American” to a plethora of other identities already at their disposal could only be a good thing.
China. Would China fight a war against the US over Taiwan statehood? Maybe, but given Russia’s poor showing in Ukraine, the war would end quickly, at least from a Taiwanese statehood perspective. The CCP’s military has no fighting experience, unproven tech, unproven hardware, and…no fighting experience. The worst that would happen, I think, is that the CCP threatens war, maybe sends some warships to the strait, maybe fires some rockets over the island and flies some fighter jets over the island, but that’s about it. The CCP just doesn’t have the muster to fight a war against the United States over Taiwan.
These four objections are so common that I can’t help but be exasperated by their banality, especially given the rich tradition of republican security theory and federalist thought over the past three or four thousand years. There are two reasons for Americans, and especially libertarians, to support Taiwan’s federation with the US:
The free riding problem. The first thing that all libertarians complain about when it comes to “foreign policy” is the free riding problem. This is a problem in political economy where agents will enjoy the benefits of a policy at the expense of other agents who are required to bear the costs. Libertarians aren’t wrong to complain about the free riding problem. It’s a big problem. Think of a Russian attack on NATO ally Lithuania.
Taiwan has a fairly hard guarantee of US military support were the Communist Party of China to attack it. This, the argument goes, allows Taiwan to be a bit more reckless than it otherwise would be when dealing with Beijing. Therefore, according to non-interventionists, the US should simply stop guaranteeing Taiwan’s military security and just trade with the people of the island instead. It would be an awful scenario to face were Taiwan to goad China into attacking it and thus draw the US into a war with China.
Federating would end the free riding problem once and for all. Taiwan’s citizens would be American citizens. They would benefit, and pay the costs, associated with such citizenship.
Sovereignty. Taiwan is not a sovereign nation-state, as China has blocked all of the island’s attempts to become so, and it never will be so long as nation-state status depends upon recognition by large states such as Russia and China (as well as the US). This actually makes it easier for Taiwan to join the republic. The American senate is a tool of international diplomacy that was utilized to bind independent states together in a federal union by trading their sovereignty for seats in a powerful upper house of Congress. Taiwan wouldn’t have to go through the arduous process of debating whether or not its sovereignty is worth the price of admission into a North American federal order, because its status as a Westphalian sovereign nation-state is non-existent.
By incorporating Taiwan into its federal order, the US could revamp the liberal world order, and it could do so by adhering to the principles which made it a beacon for liberty in the first place.
The Federation of Free States: Growing pains
We’re continuing our thought experiment on adding more states to the American republic.
Our initial experiment added 29 states to the union in 2025. After a few decades of relative success (the entire world grew economically from 2025 to 2045), the bicameral Congress of free states was willing to accept several new members, who in turn were willing to trade their sovereignty for two seats in the Senate. The polities that joined the federation of free states in the second peaceful geographic expansion of the Philadelphian federal order were varied, but only somewhat predictable. The Madisionian compound republic rearranged the map once again. Here is what it looks like in 2045:

As you can see, most of the expansion came in North America, East Asia, and West Africa. The experience of Canaan, England, and Wales hasn’t been bad, but enough nationalist-secessionist sentiments remain in these three “states” that none of their neighbors thought that giving up their sovereignty for Senate seats was worth it. All three economies grew, and peace finally came to Canaan, but if peace, wealth, and security from predation were the only things that people wanted then we wouldn’t be people. We’d be something else entirely. People want freedom, and the compound republic – the federation of free states – did not yet show in 2045 it was capable of extirpating the menace of nationalism from human existence.
The success of the ranching states of Mexico – Coahuila, Tamaulipas, and Nuevo León – within the United States prompted several more Mexican states to apply for statehood, but the pushback against too many states joining the union was stern. Yucatán and Chihuahua were added as is, giving the Senate four more seats, but the states of Zacatecas, Durango, and San Luis Potosí had to combine into one state (they called it San Luis Potosí, and it’s about the size of Nevada) in order to join the Philadelphian world order.
The prairie provinces of Canada also did well for themselves since 2025. So well, in fact, that five more provinces applied to join. However, Congress did not want to add five more states with such sparse populations, so the Atlantic provinces of Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Newfoundland, and Labrador merged to become a state that they called Nova Scotia, a massive landmass with enough people for only one or maybe two representatives. By the way, from 2025 to 2045, several old American states — Washington, Oregon, and Vermont – all held referendums on whether to leave the Madisonian republic and join Canada (or go it alone), but the referendums have proved to be unsuccessful.
Liberia’s success in the American federation is perhaps the most encouraging progress of all. Crime rates skyrocketed once Liberia joined the union, but this only shows how the American legal system does such a wonderful job of protecting property rights. Violent crime dropped, but crimes involving property rights reached an all-time high, which means that property rights in Liberia are finally being protected by a state strong enough to do so. The GDP (PPP) per capita of Liberia quadrupled from 2025 to 2045. Several neighboring states took notice, but only one, Sierra Leone, joined the federation outright.
Several Nigerian and Ghanaian polities joined the republic. All of the polities started out as administrative units within Ghana and Nigeria, and there were too many that wanted to join. So, they borrowed from San Luis Potosí’s playbook and merged with each other before applying for statehood as larger polities. From Nigeria, the states of Oyo (made up of five Nigerian states), Biafra (made up of eight states), Benin (made up of four states), and Bayelsa (three states) all joined. The states are all from the south of Nigeria.
Ghana sent three states to the republic: Ashanti (made up of five Ghanaian provinces), Volta (made up of three provinces), and Cape Coast (three provinces). The 11 provinces that made up the three new states were all from Ghana’s south. It should be noted the the Ashanti region had a relatively strong sense of nationalism when it applied for membership to the federation, and that the extirpation of this nationalism in exchange for self-government in a compound republic was not a problem for its inhabitants.
Colombia and Panama. The Caribbean experience has had less of a “wow factor” than Liberia or Mexico. Economic growth in Antilles was a little bit better than the regional average, but not by much. The big change was demographics, as many seniors from the original 50 states moved to Antilles, and many young people from Antilles moved to the original 50 states. The crime rate was similar to that of Liberia, too, with violent crimes dropping but property crimes increasing a little bit. Most of the countries in Central America (sans Costa Rica) and all of the Pacific countries in South America applied for membership in one form or another. However, only four states were added in 2045: three from Colombia and the whole of Panama. The four states got together and pulled out a map of 19th century Gran Colombia to put together a plan for federation. Isthmo (Panama), Cundinamarca (made up of eight Colombian states), Magdalena (made up of six states), and Cauca (five states) all joined the federation of free states.
Things went so well in East Asia and the Pacific that the entire country of Vietnam applied lock, stock, and barrel. Like Japan, South Korea, and the Philippines in 2025, Vietnam had too many states for the federation so six regions joined instead: Bắc Trung Bộ, Bắc Bộ, Tây Nguyên, Đông Nam Bộ, Tây Nam Bộ, and Đồng Bằng Sông Hồng. The Vietnamese now enjoy the military and economic benefits that come with being federated with the compound republic of the United States.
Further thoughts
The Canadian and West African states are the only ones with English-language speakers. Nevertheless, English continues to be employed as the lingua franca of the federated polity. This has produced a class division between those who can speak English and those who cannot, and eventually English will be spoken by nearly everybody in the polity (now numbering just over one billion souls), but the native languages are unlikely to disappear. They’ll continue to evolve on their own lines, and most people in the federation will simply be able to speak more than one language. The English of the Constitution and Bill of Rights will no doubt become antiquated as English evolves, but it’s already pretty antiquated today (2022) and there’s been no real challenge in 250 years to English’s status as the lingua franca of the republic.
Reactions to the compound republic from other states
Perhaps the most interesting aspect of the United States’ decision to apply federation to its foreign policy is the reaction of other states. The Russians, who it could be argued had an alternative to the Westphalian order in the 19th century (and this is why it pursued its own foreign policy agenda throughout the Cold War, rather than for the exportation of the Revolution), are still doing what they’ve been doing since 2000: recognizing small states along their vast border and slowly chipping away at the losses of their empire. States such as Donetsk, South Ossetia, and Crimea are recognized as states by Russia, Belarus, and, say Kazakhstan, but in 2045 the compound republic decided to build upon its foreign policy of federation by recognizing these claims to independence. This means that post-Soviet states like Ukraine and Georgia lose territory, but it doesn’t necessarily make Russia stronger and it doesn’t mean freedom is in decline. Out of two states (in this example), five now exist, and there’s nothing to suggest that they won’t lean on the compound republic rather than the Russian Federation.
The CCP turned inward, especially once the compound republic called its bluff on Taiwan. Like Russia, it has been argued that an alternative state system to Westphalia existed prior to 19th century European imperialism. The Belt and Road Initiative was supposedly part of the Tianxia state system, but regardless of whether or not you buy this argument (I don’t), China’s expansion ceased once Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan joined the Philadelphian union. The CCP became even more repressive and paranoid. The non-Han grew more despondent, and the non-Mandarin speaking Chinese, especially those living along the wealthy seaboard of the South China Sea, grew angry.
The Europeans and their interstate system continued to try to keep the Westphalian European Union alive, but without the abrogation of state sovereignty, the EU continued to be ineffectual. The French, taking a page from the American playbook, revived an old effort to federate with its former colonies. The French continued to adhere to a Westphalian logic in this effort, and the French Union floundered as badly as the European Union. The key to Madisonian compound republic’s success has been its abrogation of state sovereignty (which is “traded” for seats in the Senate). Portugal reached out to Brazil and Angola to discuss a Lusophone federation, and ties became closer, but Westphalian sovereignty trumped all discussions of cooperation and the Portuguese found themselves in the same situation as the French: members of two ineffectual confederations that are built upon Westphalian nation-state sovereignty.
The remnants of the British and Spanish Empires (Peru, Argentina, Australia, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, New Zealand, Iraq, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, the British Caribbean, etc.) continued along the same path as the Europeans. Economic growth continued at its slow pace, but compared to the societies living within the compound republic, it was becoming clear that the Westphalian remnants were losing ground, especially in regards to liberty, equality under the law, and democratic governance.
In 2045, the American republic added 22 more states, making the federation a conglomerate of 101 “states” and the District of Columbia. Liberty is on the rise, and despotism is getting cornered.
“Federations, coalitions, and risk diversification”
[…] while we recognize that issues of participation in a coalition involve complex factors, there has been little discussion in the literature from a risk-sharing perspective. It is well-known in financial economics that the pooling of resources and the spreading of risk allows investors to realize a rate of return that approaches the expected rate. We take this to be a natural motive for federation formation among a group of regions. Indeed, the existence of an ancient state in China (the example given in the next section) supports our intuition. It appears that floods, droughts and the ability of a centralized authority to diversify risk paved the way for the unification of China as early as 2000 years ago. Thus, our approach is not empirically irrelevant.
Click the “pdf” tab on the right-hand side, not the “buy PDF” tab.
Supranational (political) entrepreneurs
[…] the basis of the functional (Coasian) theory of international regimes advanced by Robert Keohane: If interstate transaction costs were very low, relative to the gains at stake for each actor, decentralized negotiation among voluntary actors with property rights would generate efficient outcomes. In summary, we may define informal supranational entrepreneurship as exploitation by international officials of asymmetrical control over scarce information or ideas to influence the outcomes of multilateral negotiations through initiation, mediation, and mobilization. […] Most existing studies of entrepreneurship fail to address this central puzzle. They focus on characteristics of supranational entrepreneurs and their actions, not the nature of alternatives.
The link (pdf) is here, and it’s a good read despite the jargon. You’ll notice that neither the Federalist Papers nor Hayek are cited in the piece. Libertarians have a chance to become relevant again in international affairs, if only they came to re-embrace the ideas of Madison, Smith, and Hayek, by abandoning non-interventionism and alliance free-riding and recognizing that federation is both a foreign policy and a type of government.
Libertarian foreign policy for the 21st century
American libertarians are behind the times when it comes to foreign policy (also known as “international relations”). We’re still, to a large extent, stuck in a Cold War mentality. The non-interventionism of Murray Rothbard and Robert Higgs is still prevalent in our circles, but this non-interventionism is rooted in the bipolar power struggle between the United States and the Soviet Union; it’s concerned with imperial overreach rather than liberty and republican security, which is understandable given the America’s role in the Cold War (the reactionary opposite to the Soviet penchant for exporting revolution).
European classical liberals are ahead of us, as they are in a more multipolar environment than us Americans, but they’re missing something too. They think the Westphalian status quo is just fine. They point to the European Union and they say, it’s better than nothing. But the world has changed since Westphalian confederations were en vogue. How does Westphalian nation-statism answer puzzles like Somaliland or Biafra or Balochistan?
It doesn’t.
American libertarians and European classical liberals have built their exit-centric approach to international relations upon Westphalian assumptions.
I think that an entrance-centric approach to the world would be a much better, more libertarian option.